Number and shape patterns are more than simple sequences; they are the foundation of mathematical thinking. In this post, we’ll explore how to teach number and shape patterns effectively in upper elementary grades, with strategies, examples, and ready-to-use classroom tools to support student success.
Why Teaching Patterns Matter
Patterns are at the heart of mathematics.
They allow students to recognize order, predict what comes next, and generalize rules.
By observing regularities in numbers and shapes, students strengthen their logical reasoning, problem-solving, and analytical skills.
Beyond the classroom, patterns appear in real-life contexts—such as musical rhythms, architectural designs, and natural formations.
Recognizing these mathematical relationships helps students see math as an interconnected and meaningful subject.
When students explore both number and shape patterns, they also begin to make critical connections between different strands of mathematics, including number sense, geometry, and measurement.
Understanding Number Patterns
What Are Number Patterns?
A number pattern is a sequence of numbers that follows a specific rule.
This rule might involve adding, subtracting, multiplying, or dividing by a constant amount—or even combining operations.
There are two main types of number patterns:
- Growing Patterns: The numbers increase according to a rule.
Example: 2, 4, 6, 8, 10 (adding 2 each time) - Shrinking Patterns: The numbers decrease according to a rule.
Example: 50, 40, 30, 20 (subtracting 10 each time)
Understanding these patterns helps students learn to predict, generalize, and reason about numbers.
Teaching Strategies for Number Patterns
When introducing number patterns, begin with visual and concrete examples.
Using number lines, hundred charts, or manipulatives can help students see the changes in each step of a sequence.
Once students are comfortable recognizing patterns, guide them to describe the rule that defines the sequence.
Encourage them to express the rule in words (e.g., “add 5 each time”) and in numerical or algebraic form.
Next, introduce tasks involving missing terms or predicting future numbers to develop a deeper understanding.
To support differentiation, use a combination of multiple-choice and open-ended activities.
For structured practice, resources like Growing & Shrinking Number Patterns Worksheets provide a balanced mix of recognition and reasoning problems.
These worksheets enable teachers to review addition and subtraction-based patterns while effectively tracking student progress.
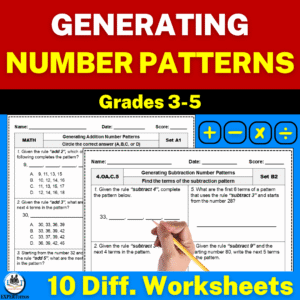
Moving Beyond Recognition: Generating Number Patterns
What It Means to Generate Patterns
While recognizing number patterns is important, generating them takes learning to the next level.
To generate a pattern, students apply a rule to create their own sequences.
This process strengthens their conceptual understanding of operations and relationships.
For example:
- “Start at 4 and multiply by 3 each time.” → 4, 12, 36, 108
- “Begin at 100 and subtract 8 each time.” → 100, 92, 84, 76
By creating their own patterns, students become active problem-solvers who can transfer their understanding to new contexts.
Instructional Approaches
To teach pattern generation effectively:
- Model a few examples with clear rules.
- Invite students to describe what happens at each step.
- Encourage them to invent their own rules and challenge classmates to identify them.
- Use all four operations—addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division—to create variety and depth.
Students who generate number patterns are developing early algebraic thinking.
They learn to see how numbers change systematically and how one operation affects another.
The Generating Growing & Shrinking Number Patterns Worksheets offer differentiated activities for practicing these skills across all operations.
Each worksheet set includes answer keys and data trackers, making assessment and monitoring seamless for teachers.
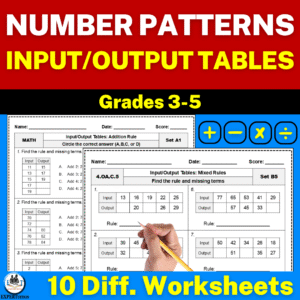
Using Input-Output Tables to Explore Functional Relationships
The Role of Input-Output Tables
Input-output tables, also called function tables, help students organize data and identify mathematical rules between two quantities.
For example:
| Input | Output |
| 2 | 6 |
| 4 | 12 |
| 6 | 18 |
Here, students can recognize the rule “multiply by 3.”
Working with input-output tables builds students’ ability to generalize and connect arithmetic patterns to early algebraic concepts.
Instructional Strategies
To teach input-output tables effectively:
- Provide examples that use a consistent rule for addition, subtraction, multiplication, or division.
- Have students describe the relationship in their own words.
- Challenge them to fill in missing inputs or outputs to reinforce logical reasoning.
- Encourage pattern extension—what happens if the sequence continues?
Engaging activities such as “Guess the Rule” games make this concept interactive and fun.
For structured practice, Number Patterns: Input-Output Tables Worksheets provide both multiple-choice and open-ended problems.
These worksheets help students transition smoothly from simple numerical patterns to function-based reasoning.
Exploring Shape Patterns
Understanding Shape Patterns
Shape patterns are visual sequences that change according to a specific rule involving color, size, or the arrangement of shapes.
They can be categorized as:
- Repeating Patterns – The same sequence repeats.
- Growing Patterns – The number or size of shapes increases.
- Shrinking Patterns – The number or size of shapes decreases.
Recognizing these visual patterns develops students’ ability to generalize rules in non-numerical contexts.
Instructional Value
Teaching shape patterns strengthens spatial reasoning, visualization, and logical thinking.
It helps students transition from concrete, hands-on math to abstract reasoning.
Shape patterns are particularly effective in supporting geometry instruction because they connect visual learning to numerical pattern recognition.
Classroom Application
To make shape pattern lessons engaging:
- Use pattern blocks, paper shapes, or digital manipulatives for hands-on exploration.
- Ask students to continue, complete, or create their own sequences.
- Integrate discussions that link shape patterns to perimeter, area, or symmetry.
For structured and differentiated practice, Repeating, Growing, and Shrinking Shape Patterns Worksheets are ideal.
These worksheets feature multiple question formats and varying difficulty levels, enabling teachers to tailor lessons to meet the needs of their students.
Differentiation and Assessment in Pattern Instruction
Pattern instruction should be accessible to all learners.
Differentiation allows students to engage with the same concept at different levels of complexity.
Differentiation strategies include:
- Providing visual aids or guided examples for beginners.
- Offering complex open-ended pattern challenges for advanced students.
- Incorporating group discussions to promote mathematical communication.
Assessment can include quick checks for understanding, journal reflections, or data trackers to monitor progress over time.
Resources that include answer keys and tracking sheets—like the worksheet sets mentioned—make this process efficient for teachers.
Making Patterns Meaningful
Connecting patterns to real-life contexts enhances student engagement.
Encourage learners to find patterns in nature, art, and architecture.
Ask them to explain why a sequence follows a particular rule—this strengthens reasoning and communication skills.
Collaborative projects, such as designing pattern-based art or creating math games, make learning interactive and memorable.
Conclusion: Building a Foundation for Algebraic Thinking
Teaching number and shape patterns is more than a unit in the curriculum—it’s the cornerstone of mathematical reasoning.
When students explore, describe, and generate patterns, they learn to think logically and recognize relationships that extend far beyond arithmetic.
With the right mix of conceptual understanding, hands-on practice, and structured activities, every student can master patterns and develop confidence in mathematics.
If you’re looking for ready-to-use, differentiated practice, explore the Number and Shape Pattern Worksheet Collections designed to make teaching these concepts clear, organized, and effective for every learner.
SAVE WITH THE BUNDLE (20% OFF)
-
Product on sale
 Original price was: $ 14.00.$ 11.20Current price is: $ 11.20.
Original price was: $ 14.00.$ 11.20Current price is: $ 11.20.